

The minimum angular separation θ (in radians) for two points to be just resolved is given by This is when the central maximum of one image coincides with the first minimum of the other. The Rayleigh criterion is when two points are just resolved. These patterns can be categorized as resolved, just resolved, or not resolved depending on the separation between the images.
The resolution of simple monochromatic two-source systemsĬonsider the diffraction pattern of two light beams diffracted by a single slit. The greater the diameter of the diffracting aperture (such as the diameter of the pupil in the human eye or the diameter of the lens in a telescope), the better resolved (clearer) the image is. When light from a point source passes through a small circular aperture, it does not produce a bright dot as an image, but rather as a diffused circular disc. The interference of light waves reflects off the top surface of a film with the waves reflecting from the bottom of the surface. Interference between light waves is the reason that thin films, such as soap bubbles, show colorful patterns. Is the condition for angles at which constructive interference occurs (maximum) where d is the distance between gratings and m is the order of the maximum. However, the angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double-slit. Diffraction grating interference patternsĪ diffraction grating is the tool of choice for separating the colors in incident light. Multiple slit and diffraction grating interference patterns. The single-slit profile is said to modulate the double-slit pattern. A true double-slit would exhibit closely spaced dark and light areas (fringes) superimposed over the single-slit pattern. The previously section shows an ideal double-slit which ignores the single-slit characteristics of each of the two single-slits. Modulation of two-slit interference pattern by one-slit diffraction effect. 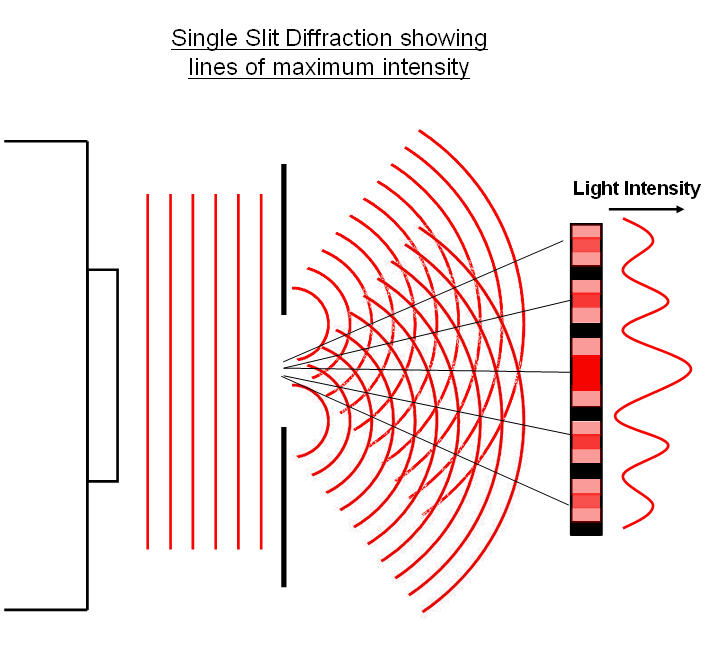
Where λ is the wavelength, m is the order of the maximum, D is the distance of the slits to the screen, and d is the distance between the two slits.

Where λ is the wavelength, m is the order of the maximum, D is the distance of the slits to the screen, and a is width of the slit. Where λ is the wavelength and a is the size/length of the slit The angle of diffraction for the first minimum θ can be given by We can represent this diffraction pattern by plotting the light intensity against the angle of diffraction. Special diffraction patterns appear when light is diffracted by a single slit which is comparable to the wavelength of the light in size. Total energy (KE+PE) remains constant throughout the motion.At minimum displacement, PE is at max while KE=0.At zero displacement, KE is at max while PE=0.At maximum displacement, PE is at max while KE=0.However, the total energy remains constant. In a SHM, there is an interchange between KE and PE throughout the motion. The angular frequency ( w ) is related to the period of the SHM by the following equation Where x0 is the amplitude (maximum displacement), x is the displacement, v is the velocity, and a is the acceleration. 9.1 – Simple harmonic motionīy Newton’s Second Law, SHM can be defined as the following equations







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
